Windows 11 Task Manager is a tool that is part of the Windows operating system. It provides a handy overview of all running processes and programs and helps you manage your system, stop tasks and analyze performance. To open the Windows 11 Task Manager, there are several ways: via the Start menu, a Windows shortcut or the Run dialog box.
Windows Task Manager was first developed in 1996 and released as part of Windows NT 4.0 and Windows 9x. The task manager as we know it today appeared with Windows 8, where it already offered a overview of CPU, RAM, Ethernet and Wi-Fi as well as tabs like “Process”, “Performance” or “History”. Since Windows 10, the “Processes” tab is divided into different categories for current tasks like “Application”, “Background processes” and “Windows processes”.
The advantage of the task manager: you can view process details or terminate selected tasks if necessary. So Task Manager is recommended to make Windows 11 faster. It also allows to monitor the performance of the processor in order to spot the resource-intensive tasks and underlying programs. It is even possible to identify suspicious activities, foreign to Windows, as well as malicious software.
Open Windows 11 Task Manager¶
Method 1: Windows Shortcut [Ctrl] + [Alt] + [Suppr]¶
In recent versions of Windows, the Windows shortcut [Ctrl] + [Alt] + [Suppr] opens a full-screen menu with commands such as “Sign Out”, “Lock” and also “Task Manager”. Click on this last point to open the task manager of Windows 11.

Method 2: Windows Shortcut [Windows] + [X]¶
The Windows shortcut [Windows] + [X] takes you to quick start menu with main Windows functions. In the list of menus, you will find the task manager that you will only have to open by double-clicking on it.
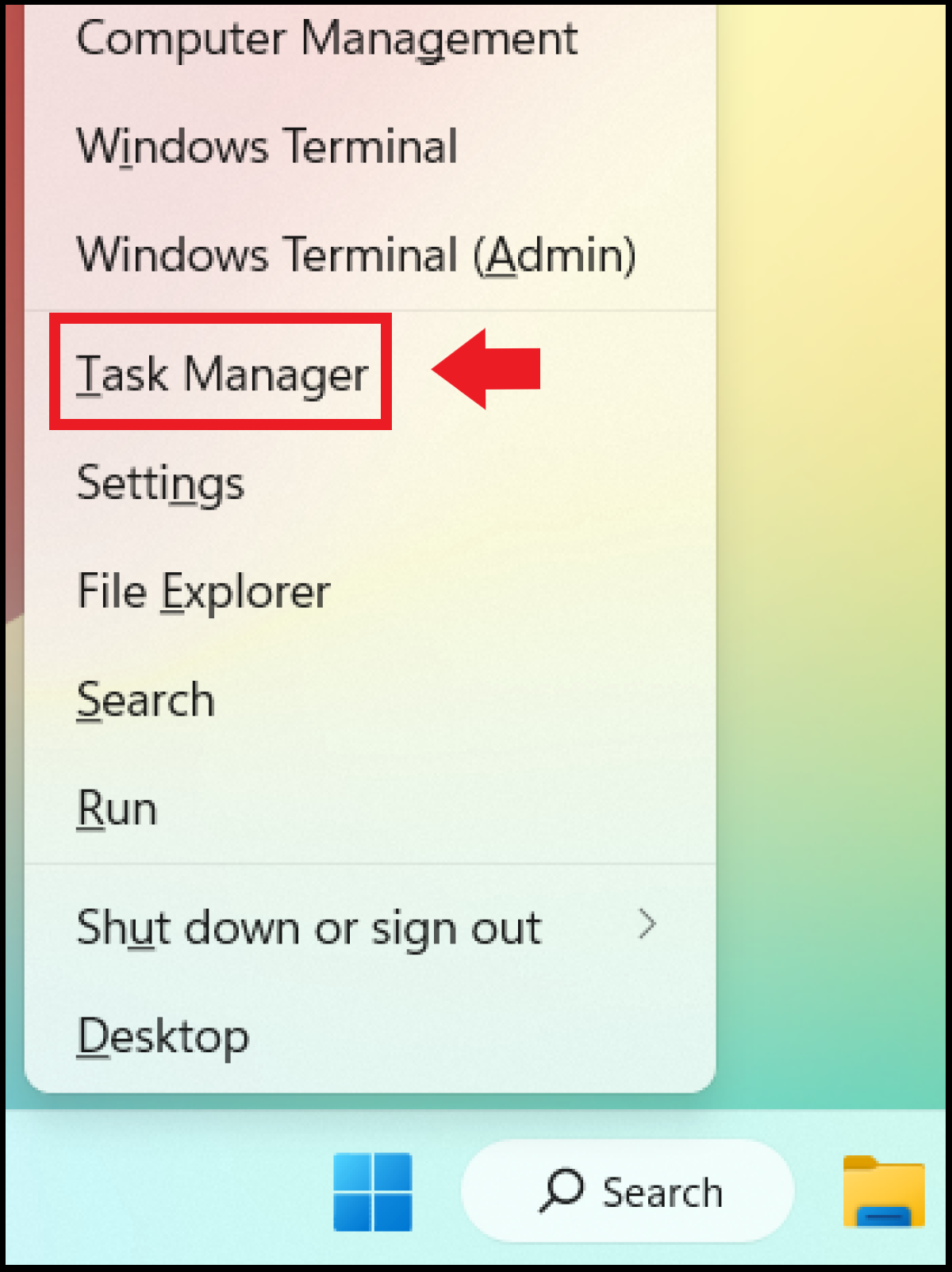
Method 3: Windows Search¶
Type “task” in the Windows search bar and open the task manager app from there.
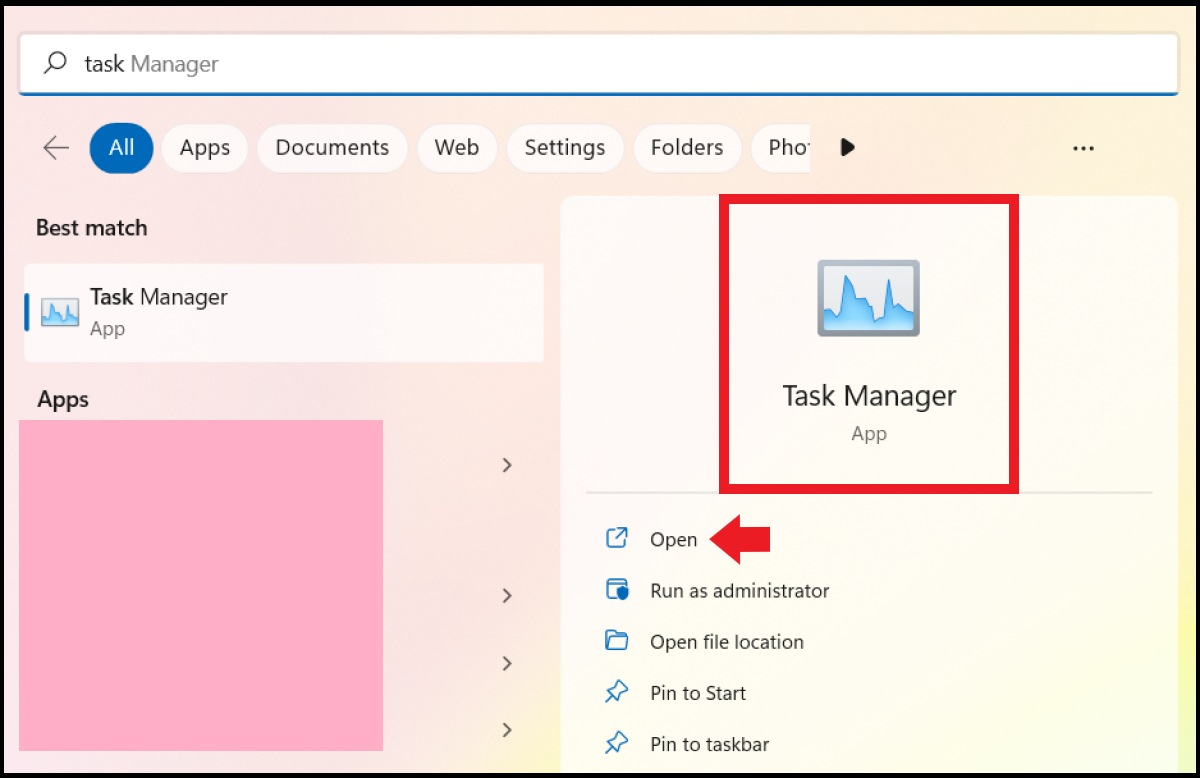
Method 4: Run Dialog¶
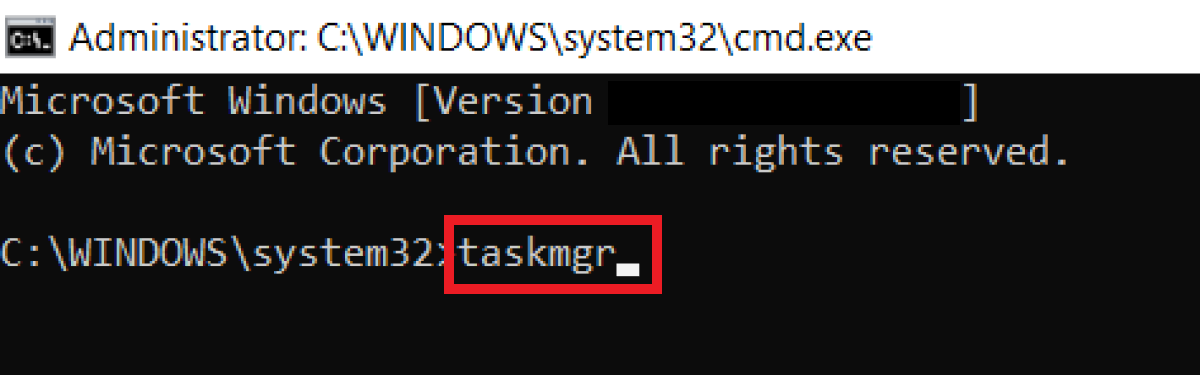
Step 1 : the Run dialog is more complicated than the previous methods, but it can be useful if the touchpad or mouse aren’t working. Invoke the command prompt with [Windows] + [R] and type “cmd”.
2nd step : launch the Run as administrator dialog with [Ctrl] + [Maj] + [Entrée]. Then enter the CMD command “taskmgr” and confirm with [Entrée] to start the task manager.
End Tasks with Task Manager¶
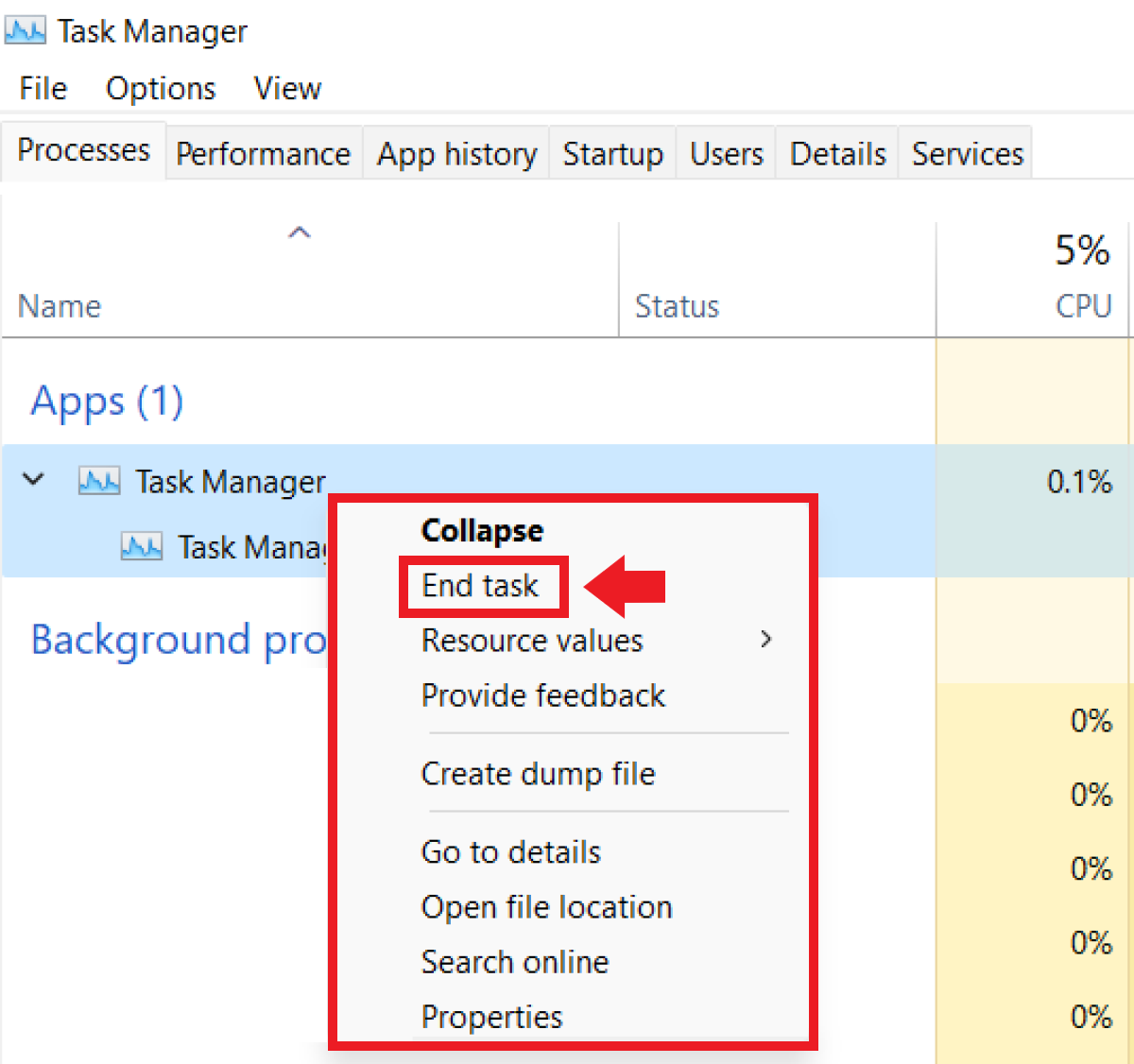
If you want to end tasks, open Task Manager, select a process under the “Processes” tab and right click on it. You then see a list with different options like “Develop”, “Debug” or “End task” to stop the task immediately. In this case, select “Complete task”.
These tabs are available in Windows 11 Task Manager¶
After opening the task manager, you will find seven different tabs that allow you to take a look at active processes, performance history as well as information about users and autostart programs.
You will find the following tabs in the task manager:
- Process : displays active applications, background processes, Windows processes as well as detailed information on the respective consumption of CPU, RAM, data carriers, network, GPU and current; a right click on the processes allows among other things to stop or restart them.
- Performance : shows using a real-time graph the use of CPU, RAM, data carrier or wireless network.
- Application history: provides an overview and history of resource usage by apps in the current user account.
- Starter app: shows all current applications in Windows 11 Autostart, i.e. all applications that automatically launch each time Windows starts; Here you have the option to uninstall unnecessary apps to make Windows 11 faster.
- Users: displays all currently logged in user accounts and their resource usage; Clicking on the account will show you a list of all active apps and processes in the account.
- Details : displays the full list of all processes, including name, status, CPU, and description.
- Services : provides a list of all applications used to manage the computer; for each application there is information about the current status, PID, description and application group.