The right to be forgotten: in May 2014, the Court of Justice of the European Union (CJEU) in Luxembourg ruled that search engines like Google should allow its users to delete search results. It must be sensitive personal data, that is, which is false, abusive, outdated or irrelevant.
Delete personal information from Google: explanation of the form to fill out¶
If your request falls under the right to be forgotten, completing this form will allow you to remove your sensitive personal data from Google.
Step 1 : open it personal data deletion request form from Google.
2nd step : indicate the country in which the law applies. In most cases, this is the country in which you reside.
Step 3: you must now enter your name and email address. To complete the form on behalf of another person, you will need to specify the relationship between you and that person, and be able to prove that you are authorized to represent that person.
Step 4: Now indicate which websites you want removed from search results. Use the URL you get from Google search results for this. If you want to report multiple addresses, enter one URL per line.
Step 5: specify why this link should be removed from search results. You must enter a justification for each URL listed. Again, use one line per justification.
Step 6: enter the name under which you or the person you are applying for can be found on Google.
Step 7: finally, confirm that you agree with the data processing and that all the data indicated are correct. Finally, enter the current date and your name and send the request.
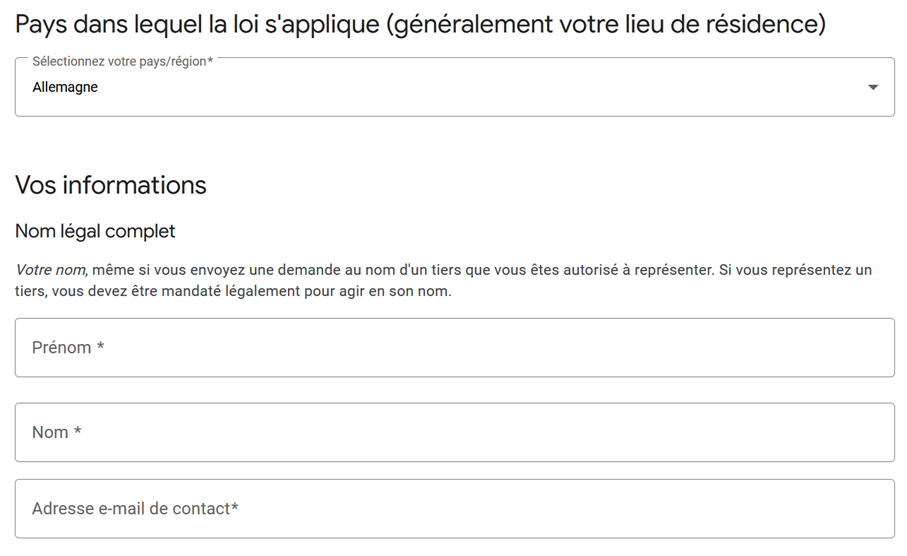
must be completed. / Source: https://reportcontent.google.com/forms/rtbf To have personal data deleted on Google, the search engine offers several forms. These depend on why you want to have this sensitive information deleted. The right to be forgotten, outdated data or non-consensual pornography can be valid reasons, for example. Google has created a help page on the subject“Remove information from Google”
. You will also find the links to the corresponding forms there. Once this form has been completed and sent, the data will not have disappeared from the Internet. It is the search result entries that are deleted, i.e. the links that appear in search engine result lists. The information itself is still searchable, but it’s not as easy to find anymore. You can therefore make this deletion request on other search engines: Bing, for example, also has arequest form to block search results
.
Google: how does the right to be forgotten work?
In 2014, the Court of Justice of the European Union (CJEU) ruled in favor of a Spaniard who asked Google to remove links to articles about him. The information contained in the newspaper article was long out of date and the complainant believed that it damaged his reputation. The ECJ upheld this decision and Google had to remove the link.I’ stop Google Spainhas therefore allowed this idea of the right to be forgotten to be integrated into the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) of the European Union. I’ GDPR article 17 is devoted toright to erasure of personal data on the Internet. Google is obliged by law to prevent the sharing of this information by removing links to the corresponding data. The Federal Data Protection Act also contains information on this in theGDPR Article 35
.Google: what should the search engine remove?
¶ Google is not obligated to act on every deletion request. In the case of public figures
like politicians, society’s interest in having information may outweigh the right to be forgotten. This right also applies mainly to natural persons; companies can only benefit from certain provisions, as they are notably limited by the tax or accounting legislation in force.
- As a general rule, it must be personal data to enforce the right to be forgotten. The following situations are considered valid grounds for requesting Google to delete personal information: Obsolete content:
- if the information is no longer relevant, but continues to negatively influence your life, Google may remove the entry. Wrong content:
- you can request the removal of links on the Internet if they contain false information. Sensitive or Reputational Damaging Content:
any harmful or defamatory information posted on the Internet may be removed from search engines to protect the person’s reputation. As the right to be forgotten derives from the GDPR, it is notapplicable only within the European Union
. Even if Google deletes the requested search results, the links will still be searchable in the United States, for example.Can I delete the entries myself?
¶
You can fill out the form to remove personal data from Google, but it is not possible to remove links on your own. Also, expect Google to take some time to review your request.However, you have another option: you can also contact the operators of the websites concerned directly. If the information there changes, the search results on Google will adjust accordingly. To speed up the modification of search results, you can use the obsolete content removal tool
from Google.Main Court Judgments
¶
In recent years, European courts regularly consider cases related to the right to be forgotten. Depending on the case, the courts accept the complaints or rule in favor of Google. The following two judgments are a good example of the complexity of the law and the fact that it is in fact rather a question of finding a balance between the interests involved.Judgment in favor of the public interest (2020)
¶
The director of a charity organization in Germany wanted to remove links to articles proving the financial deficit of the association he directed from the search results. The articles mentioned the complainant by his full name.
Both the Court of Appeal in Frankfurt am Main and the Federal Court of Justice ruled in favor of Google. Reason: the public interest in this case prevails over the right to be forgotten.Google must act on fake news (2022)
¶
A couple from the financial sector have been accused in an article of unfair commercial practices. A photo of the couple even illustrated the article. The two plaintiffs accused the website of spreading false information and therefore demanded that Google remove the links to the article as well as the photo from its search results.
The German Federal Court of Justice initially ruled in favor of the search engine. The Court of Justice of the European Union (ECJ), on the other hand, sided with the applicant couple: according to the ECJ, the court should not rule on the misleading nature of the information. Evidence proving the inaccuracy of the information simply needs to be provided for Google to remove the entries from search results.
As the EU has still not finalized the draft ePrivacy Regulation (status: February 2023), legal actions are regularly initiated in the area of this directive. This also applies to European cookie regulations. Website owners and operators should particularly keep abreast of these judgments in order to anticipate any legal disputes.