THE FEEDFORWARD NEUral Networks (FNN) are simple neural networks which exclusively transmit information from a layer to the next. They are divided into FNN Monocouche and FNN Multilayer and have different areas of application in the field of Deep Learning.
What is a Neural Network feedforward?
Neurral Network (FNN) feedforward, also called Direct Action Network in French, is a neural network made up of artificial neurons and entirely without feedback. This type of network is considered to be a particularly simple form of artificial neural network, because it still acts exclusively in a direction, without feedback. Deep feedback networks are an important element for the creation of models in the field of Deep Learning and Artificial Intelligence. Depending on the number of layers used (layer In English), we distinguish monocounches and multilayer FNNs.
AI tools
Use the power of artificial intelligence
- Create your website in record time
- Boost your activity thanks to marketing by AI
- Save time and get better results
As with any artificial neural network, the model of the neurons with direct action are vaguely inspired by the functioning of the human brain, although their architecture is much more simplified. This also processes information through a neural network. The FNN has at least two layers: an input layer (Input Layer) and an output layer (Output Layer). Between the two, there may be other layers (Hidden Layers) in any number. Each layer is exclusively connected to the follow -up that succeeds him. This connection is made by « edges ». In a neural network feedforward, all information only circulates in one direction, namely the input layer to the output layer.
- The input layer : It receives all the input data that is introduced into the neural network. Each neuron of this layer corresponds to a property of the incoming data.
- Hidden layers : hidden layers can be between the input layer and the output layer. Each hidden layer consists of interconnected neurons between the previous layer and the following.
- The output layer : The output layer gives the final result of the Neural Network feedforward.
In a neural network feedforward, the data is introduced into the input layer, where each neuron represents a specific characteristic of the inputs. These neurons apply synaptic weights information received before transmitting it. In a single layer FNN, the data goes directly to the output layer, while in a several layers in a FNN, they first pass through hidden layers, where they are again weighted and transformed. As these intermediate transformations are not visible, we speak of hidden layers.
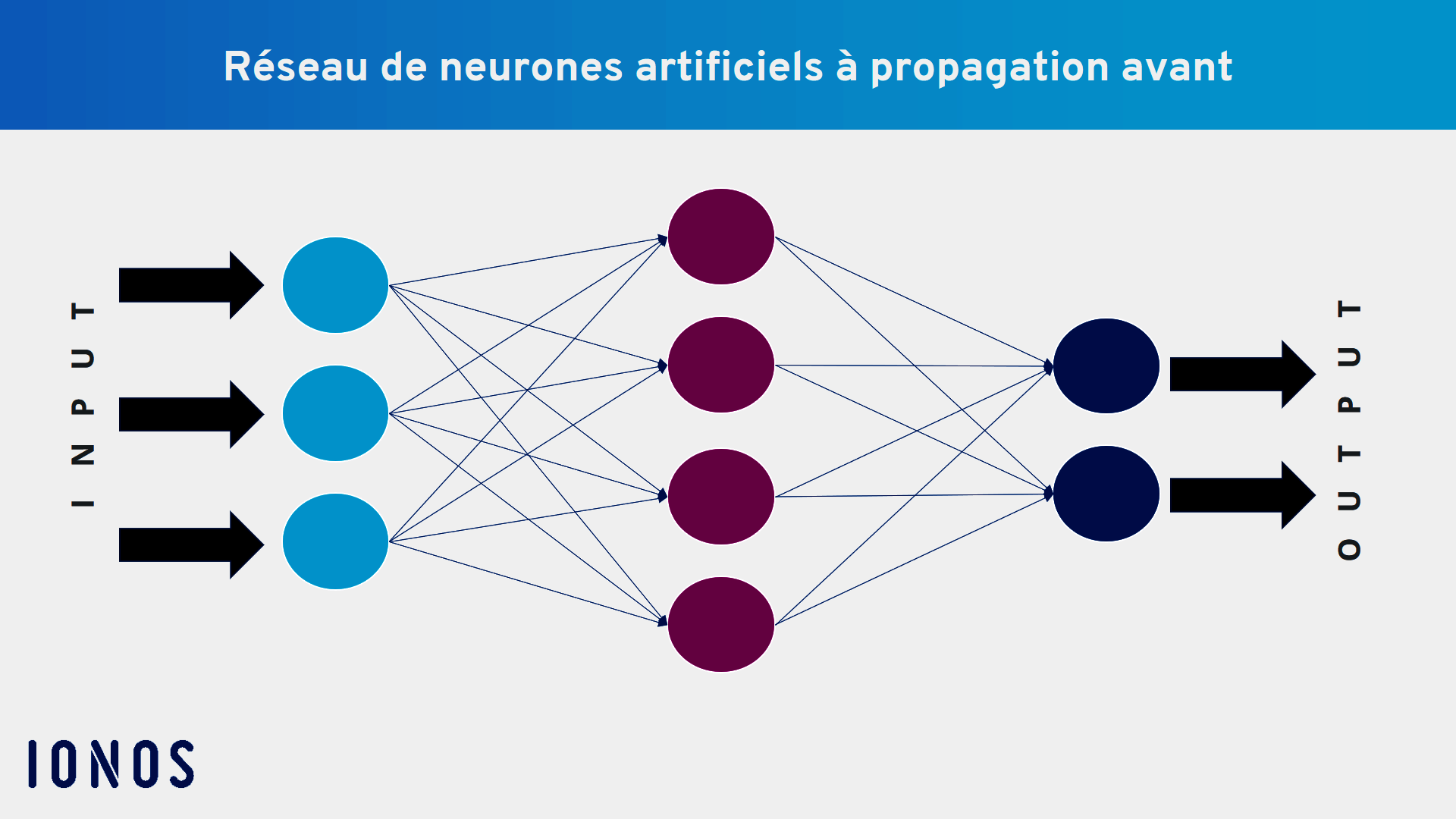

Throughout the process, weighted values are accumulated at each stage. A activation function is then applied to determine whether a neuron should transmit information or not. In some cases, a Threshold value is used for this decision. In a neural network feedforward, connections are strictly unidirectionalonly connecting a layer to the next without feedback.
What are the main areas of application?
There are many areas of application possible for neural networks feedforward. Networks have many advantages, especially when it comes to processing and connecting large amounts of unstructured data. Here are some possible areas of application:
- recognition and treatment of speech : Direct action neural networks can be used to convert text into spoken language or to convert language spoken into text.
- Image recognition and processing : You can analyze images and extract characteristics, for example by digitizing and recognizing handwritten entries.
- classification : Using neural network feedforward, the data can be classified according to defined parameters.
- the prediction : FNN can also be used for the prediction of events or trends, for example in finance and meteorology. They are used, among other things, for weather forecasts or in various early alert systems in the fields of protection against disasters, space and defense.
- Detection of fraud : Neural networks feedforward can play an important role in identifying activities or fraudulent models.
What is the difference with a Neural Network (RNN) recurrent?
The opposite of a neural network feedfforward is the Neural Network (RNN) recurrent. This certainly works in a fundamentally similar way and transmits information on neurons from the initial layer to the final layer, but can also return it. In such a network, recurring connections allow information to circulate not only forward but also to return to the previous layerswhich allows the network to keep a certain historical data processed.
Networks of this type are mainly used when the context is important in the search for results. This is particularly useful for the language treatmentwhere the context is crucial. For example, the word « opera » can designate a musical genre, a building or a pastry; An RNN allows you to correctly interpret the word according to the context of the sentence.